A new report from BloombergNEF has highlighted a pressing issue for the future of clean energy: the silver mining industry will require a staggering $2.1 trillion investment by 2050 to meet growing demand. This influx of capital is necessary to support the production of silver, a key material used in a variety of green technologies, particularly solar energy. Without this significant financial input, silver shortages could worsen, potentially driving up the costs of renewable energy technologies and delaying the global transition to a net-zero future.
The Growing Metal Deficit Problem
In addition to silver, BloombergNEF has projected looming deficits in several other crucial metals, including aluminum, copper, and lithium. These metals, along with silver, are essential for producing components used in renewable energy systems like solar panels and batteries. The report warns that these shortages could hit by as early as 2030, adding to the challenges already faced by the energy transition sector.
The silver market, in particular, has been under pressure for some time. Demand for silver has steadily increased, especially due to its use in photovoltaic cells, which convert sunlight into electricity. As more nations adopt solar energy, the demand for silver will only grow. However, with the projected shortage, this vital component could become even more expensive, complicating efforts to make solar energy more affordable.
Why Government Policies are Crucial for the Future of Battery Metals

Allan Ray Restauro, a metals and mining expert at BloombergNEF, stresses the importance of robust government policies in ensuring the success of battery metals. According to Restauro, governments must establish frameworks that guide the full lifecycle of these metals. This includes creating efficient collection networks for spent batteries, setting recovery rate requirements, and developing principles for second-life battery management.
These policies are essential in reducing waste, improving recycling efforts, and ensuring that battery metals are managed sustainably. Without such measures in place, the industry may face even greater challenges in securing the necessary raw materials, which could further impact the availability and cost of energy storage solutions like batteries.
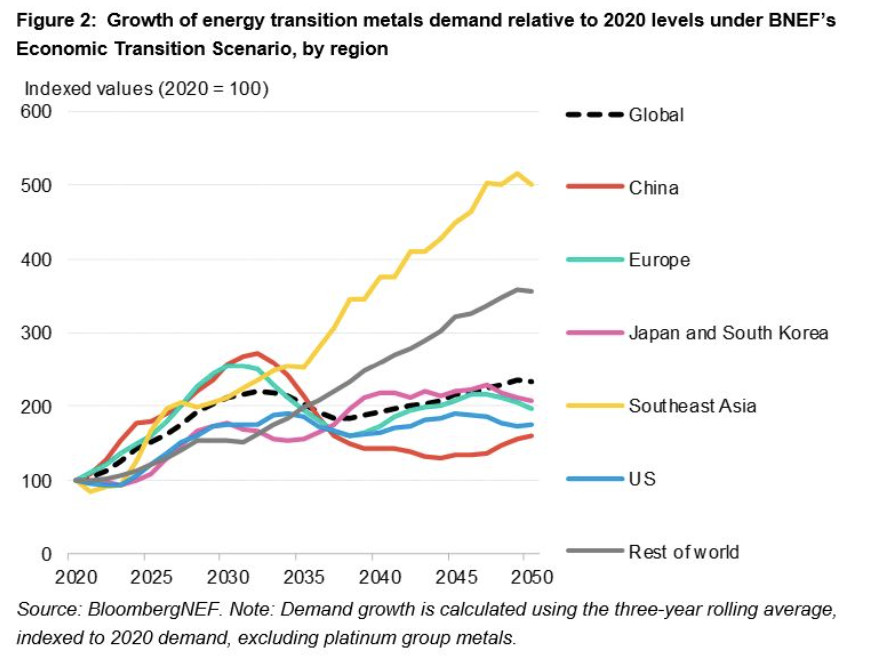
China’s Dominance in Transition Metal Demand

Another key finding of the BloombergNEF report is the rapid growth in transition metal demand, particularly in China. The country’s use of these metals has been increasing faster than the global average and is expected to peak around 2030. This growth is largely driven by China’s aggressive push toward renewable energy and its dominance in the production of electric vehicles, which rely heavily on metals like lithium and copper.
Looking forward to the 2030s, Asia as a whole is expected to become the fastest-growing market for transition metals. This region’s demand for metals will likely shape global supply chains and could further strain the availability of silver and other essential materials unless substantial investments are made.
Recycling: A Potential Solution to Ease Metal Shortages
While the BloombergNEF report paints a challenging picture of future metal availability, it also points to recycling as a potential solution to ease market pressures. Increased efforts to recycle metals like silver, aluminum, and copper could help extend their lifecycle and reduce the strain on mining operations.
Recycling not only helps to conserve raw materials but also significantly reduces the environmental impact of metal production. By reusing metals that are already in circulation, industries can lower their overall emissions and decrease the need for energy-intensive mining activities. This could prove to be a critical strategy in ensuring the long-term sustainability of the clean energy transition.
Economic Impact: What Prolonged Deficits Mean for Clean Energy

Despite these potential solutions, Kwasi Ampofo, head of metals and mining at BloombergNEF, warns that prolonged deficits in essential metals will inevitably drive up the cost of raw materials. As prices rise, the cost of clean energy technologies, such as solar panels and batteries, will follow suit. This could slow the adoption of renewable energy at a time when global efforts to combat climate change are becoming increasingly urgent.
Ampofo explains that if costs continue to climb, it could significantly hinder the pace of the energy transition, as both governments and consumers may struggle to afford the higher prices of green technologies. As a result, investments in mining and recycling will be critical to avoiding such a scenario and ensuring that clean energy remains accessible.
Conclusion
In the face of rising demand for silver and other transition metals, securing a $2.1 trillion investment by 2050 is crucial for the silver mining industry. Without this financial support, the global shift toward clean energy may be jeopardized, as shortages and price hikes could slow the adoption of solar and other renewable technologies.
To safeguard the future of clean energy, governments, industries, and investors must work together to ensure that these essential raw materials are available in sufficient quantities. This will not only help meet the world’s growing energy needs but also play a pivotal role in achieving global net-zero goals.





